Straight Leg Raising Test

Painless straight leg raising does not exclude a disc lesion.
Straight leg raising test. These tests along with relevant history and decreased range of motion are considered by some to be the most important physical signs of disc herniation regardless of the degree of disc injury. Straight leg raise test. To determine the cause of low back pain. Video demo procedure positive signs.
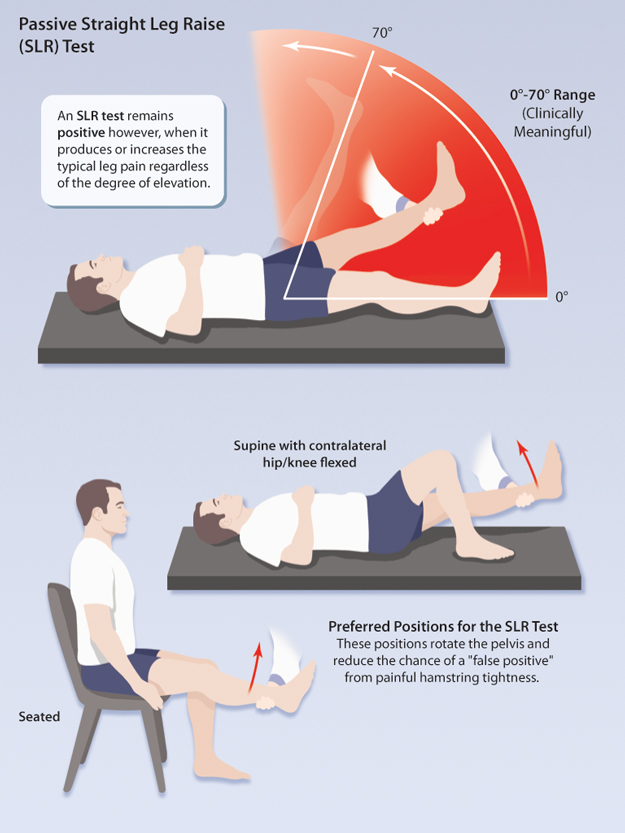
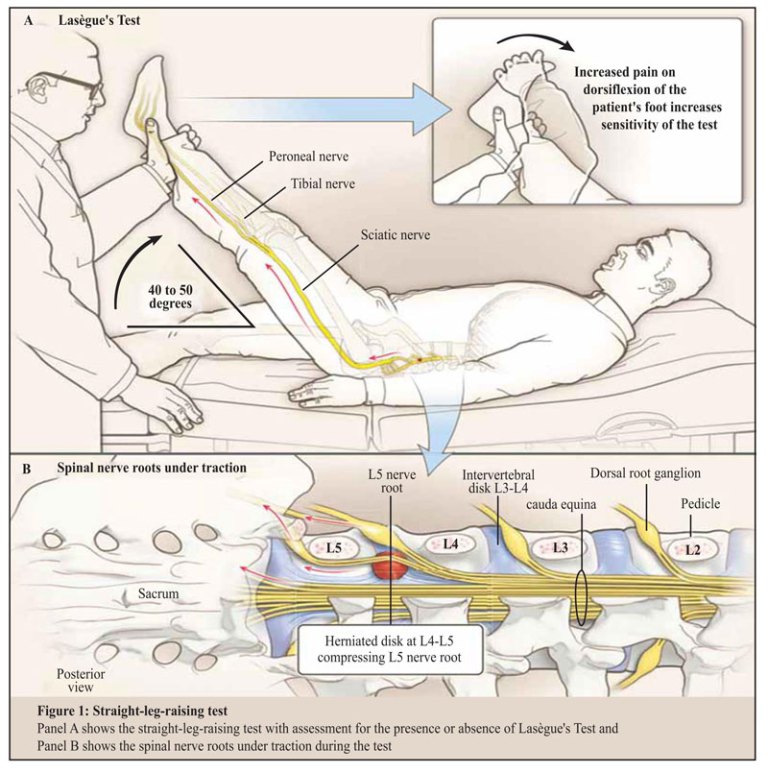
The examiner will passively flex the patient s hip while maintaining the knee in full extension. People should be able to hold the leg straight up with the heel elevated off an examination bed. The straight leg raise also called lasègue s sign lasègue test or lazarević s sign is a test done during a physical examination to determine whether a patient with low back pain has an underlying herniated disc often located at l5 fifth lumbar spinal nerve. In a systematic review of 11 studies assessing the accuracy of slr against surgery as a reference standard deville et al.
Neurodynamic tests check the mechanical movement of the neurological tissues as well as their sensitivity to mechanical stress or compression. Thus positive and negative results may be less conclusive in older patients. The straight leg raise which is also known by the name of lasègue s sign is a test done on a patient with low back pain in order assess the cause of the low back meaning that whether the low back pain is caused due to a herniated disc or some other pathological condition. Although widely used the test has limited diagnostic accuracy when diagnosing herniated discs.
This is quite an effective and accurate test to determine the cause of a low back pain. With the leg straight the patient should then raise their foot off the bed and hold it in the air. The straight leg raise slr or lasegue s sign is a widely used test to assess the sciatic nerve in cases of back pain. The discriminative power of the straight leg raise test seemed to decrease as age increased.
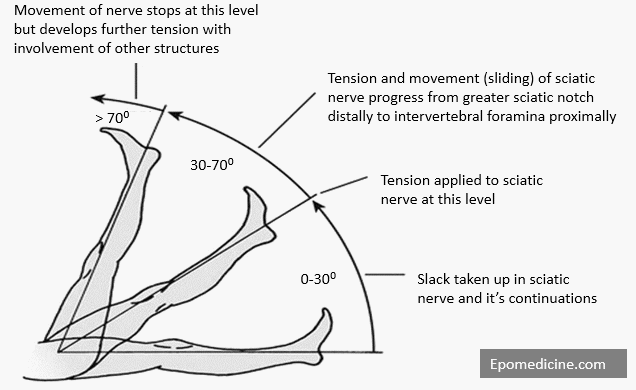
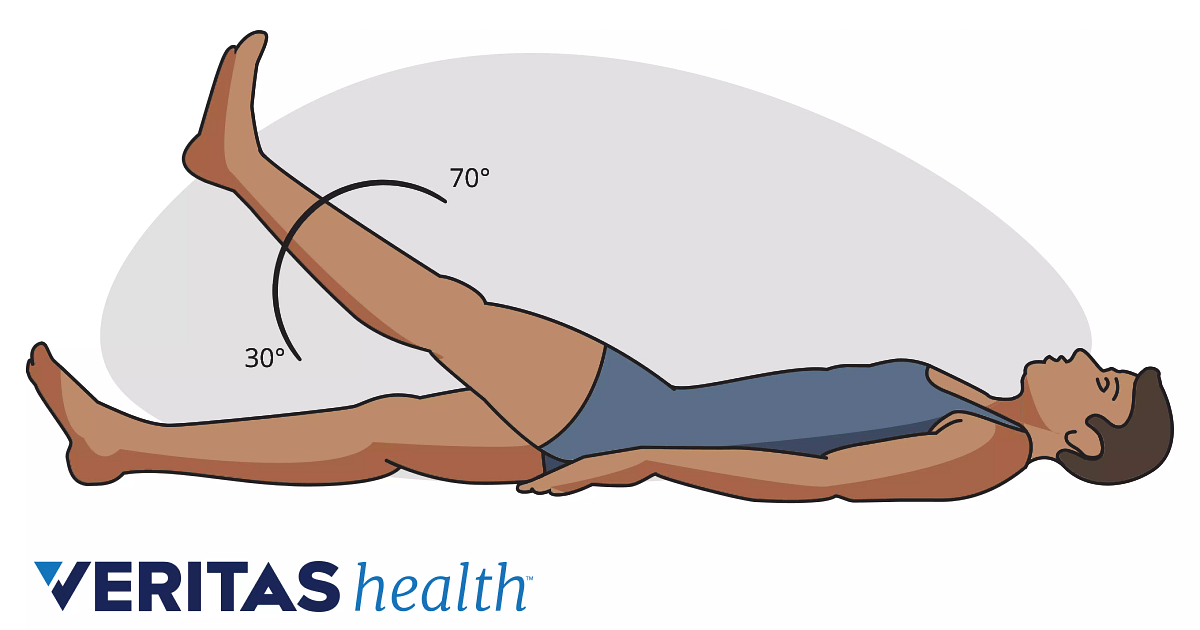
Slr test straight leg raise test. A straight leg raise test is performed by having the patient lie flat on a bed. To test for the presence of a disc herniation. Herniated disc if the patient experiences sciatic pain when the straight leg is at an angle of between 30 and 70 degrees.
The straight leg raise slr test is a neurodynamic test.